vehicle scrappage policy: Opinion: Environmental benefits of scrappage policy

By IV Rao and Aravind Harikumar
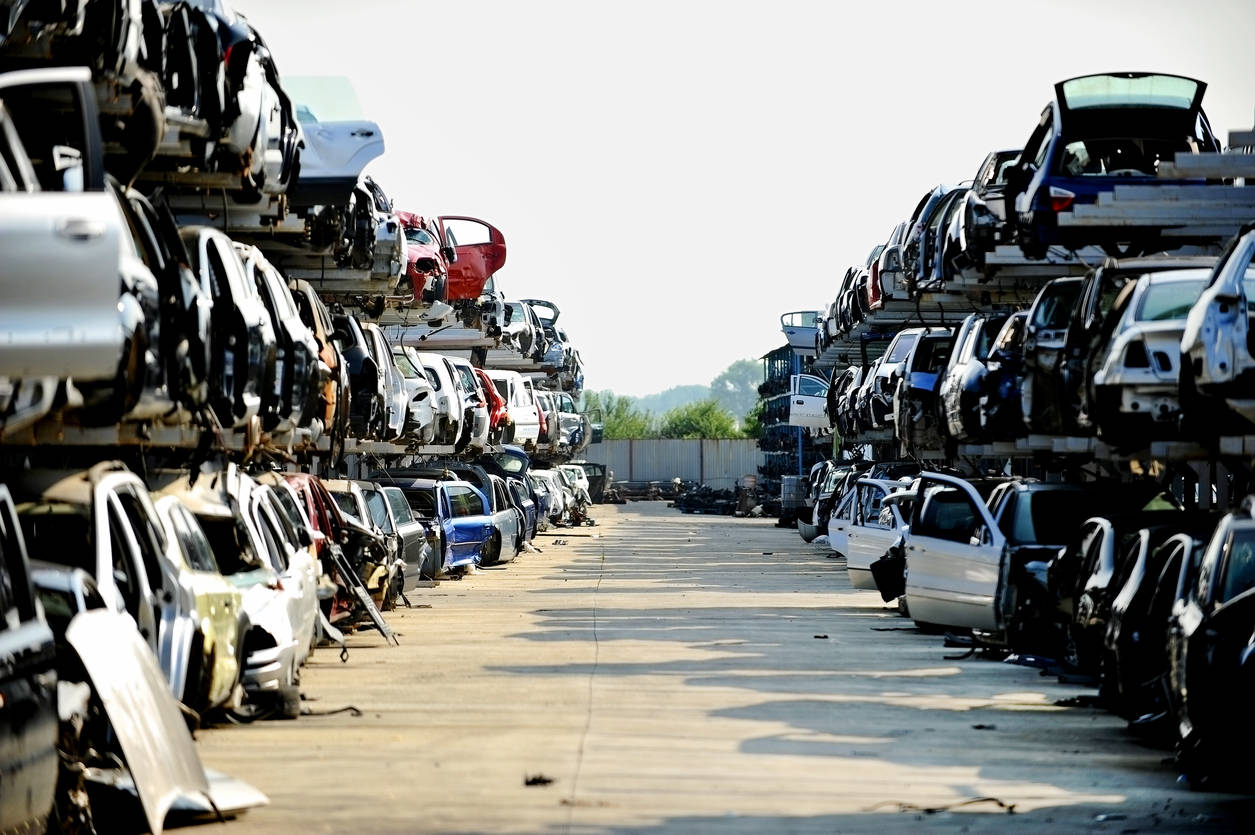
Mandated scrappage of aged cars will give us the advantage of reducing vehicular emissions, presented aged scrapped cars are changed with new, cleaner cars. An structured scrappage system can also boost resource performance by imbuing circularity in automobile production via the reuse and recycling of areas.
Numerous nations around the world such as the United States, South Korea, Japan, Germany and the Netherlands have launched temporary guidelines to scrap more mature cars for improving upon the air good quality, boosting automobile income (e.g. Britain and France in the nineteen nineties) or improving upon safety (e.g. Italy, Ireland, Argentina).
Distinctive nations around the world have followed various requirements, with ‘Age’ frequently not serving as the only requirements for classifying cars for scrappage. For instance, in France and Italy, cars earlier mentioned a specific age were being essential to be examined for emission expectations, failing which they were being mandated for scrappage, their proprietors eligible for govt incentives to obtain new cars.
Most developed nations around the world also have a set technique for deregistration and avoidance of the use of more mature cars. Therefore, primary infrastructure is required to check the automobile condition to optimise the financial and environmental rewards of obligatory vehicular scrappage.
India has the infrastructure in spot to check for idle emissions on cars for Pollution under Command (PUC). Having said that, idle emission checks might not clearly point out the mass emission general performance of these cars in use on the street.~
India has infrastructure in spot to check for idle emissions on cars for Pollution under Command (PUC). Having said that, idle emission checks might not clearly point out the mass emission general performance of these cars in use on the street. In accordance to a research by the Environment Pollution (Avoidance and Command) Authority (EPCA) in 2017, the success of PUC in checking idle emissions is also questionable.
The Nationwide Eco-friendly Tribunal (NGT) banned the use of 10-year-aged diesel cars and fifteen-year-aged petrol cars on Delhi streets. Having said that, this did not guide to scrappage of these cars as there was a demand from customers for them outside the house the condition of Delhi. Therefore, the polluted cars shifted outside the house the geographical purview of NGT’s ruling, reducing the over-all environmental effect of NGT directive. A very similar circumstance was confronted by authorities in Germany, when vehicles mandated to be scrapped observed a enormous resale market in African nations, ensuing in the export of these cars.
Despite the fact that automobile wellbeing check and certification very similar to developed nations around the world is required to implement a scrappage policy dependent on the exercise of the automobile for re-registration, it calls for huge investments from the govt/business.
Contemplating the present state of affairs in India, the criterion of ‘Age’ for employing scrappage might be the most cost efficient system to derive environmental rewards. The determine down below gives a chronological timeline of the implementation of emission restrictions in India.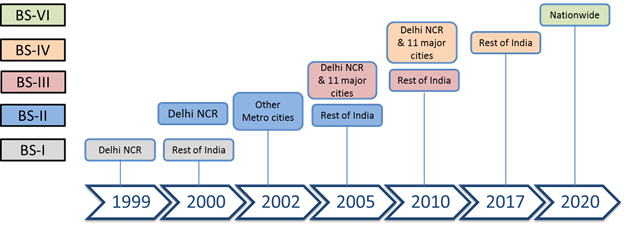
The obligatory de-registration will phase out pre-BS stage cars, BS-I cars and BS-II cars predominantly from Delhi NCR and important cities.~
If the countrywide scrappage policy in 2020 mandates scrapping of cars more mature than fifteen a long time, it would indicate de-registration of cars registered before 2005. The obligatory de-registration will phase out pre-BS stage cars, BS-I cars and BS-II cars predominantly from Delhi NCR and important cities. All BS-I and pre BS-I cars nationwide will be phased out.
A BS-I diesel vehicle emits 31 moments more PM (Particulate Subject) than a B-VI diesel vehicle and a BS-II diesel vehicle emits seventeen moments more PM than a BS-VI counterpart. At present, except for Delhi, India does not have a cap on automobile existence and a automobile might be used on the street as extended as the proprietor deems in shape.
As for each the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) estimates, pre-2000 commercial cars (CV) are dependable for over fifteen{0764260a27b4b31ca71a8adf79c3ae299a61e6f062052eee3f0df84ce9b30ade} of GHG (Eco-friendly House Gases) emissions from the CVs. CVs contribute to 73{0764260a27b4b31ca71a8adf79c3ae299a61e6f062052eee3f0df84ce9b30ade} of the emissions from the street transportation sector which in convert is dependable for about 12{0764260a27b4b31ca71a8adf79c3ae299a61e6f062052eee3f0df84ce9b30ade} of over-all emissions in India. Therefore, phasing out these aged cars will have a substantial environmental effect in phrases of reduction of pollutants from automobile exhausts.
Even however lots of other parameters need to be assessed to estimate the wellbeing of any automobile for re-registration, until the infrastructure for the similar is developed, developing ‘Age’ as the sole parameter is the finest move to optimize the environmental profit from the automobile scrapping in India.
(IV Rao is the former head of R&D and Director of Maruti Suzuki Centre for Excellence. Aravind Harikumar is a investigate affiliate, Transport & City Governance, TERI)
(DISCLAIMER: The views expressed are exclusively of the authors and ETAuto.com does not essentially subscribe to it. ETAuto.com shall not be dependable for any injury induced to any man or woman/organisation right or indirectly.)








